Aerospace Welding Test videos
tips and tricks for helping you pass the test
Group 1 - carbon and low alloy steels 1g, 2g, 3g
Group 1 2G weld test tips for D17.1 aerospace weld test
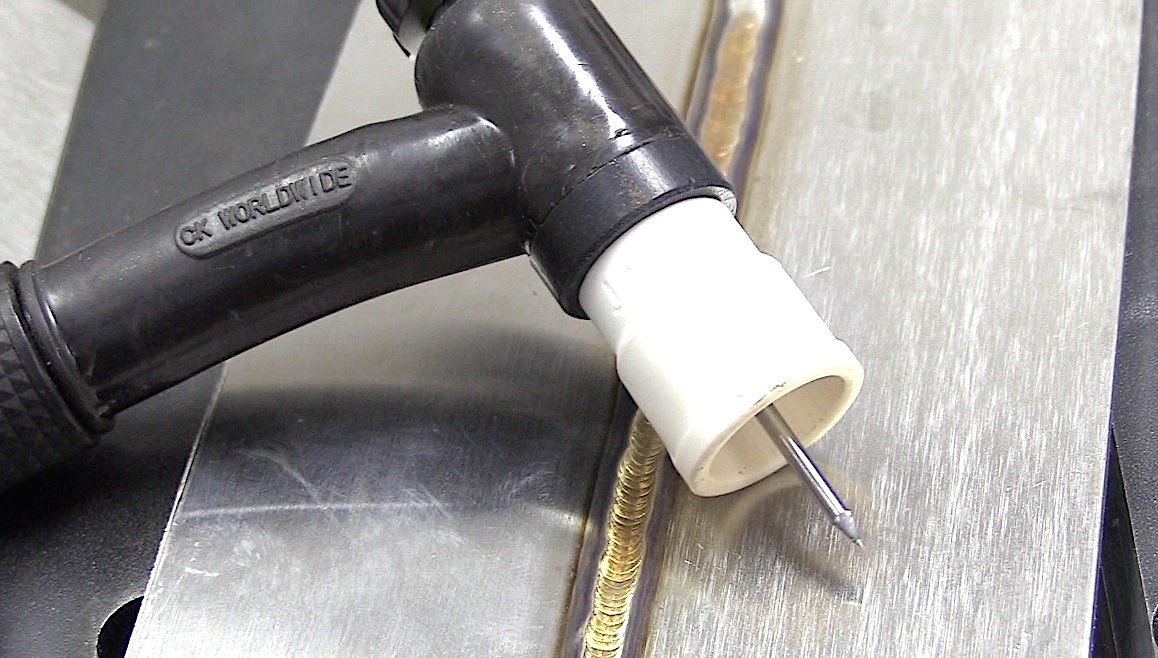
learn more about the jazzy 10 ceramic cup here
Group 2 Stainless Steel Alloys
Group 4 Aluminum alloys 1G Weld test D17.1
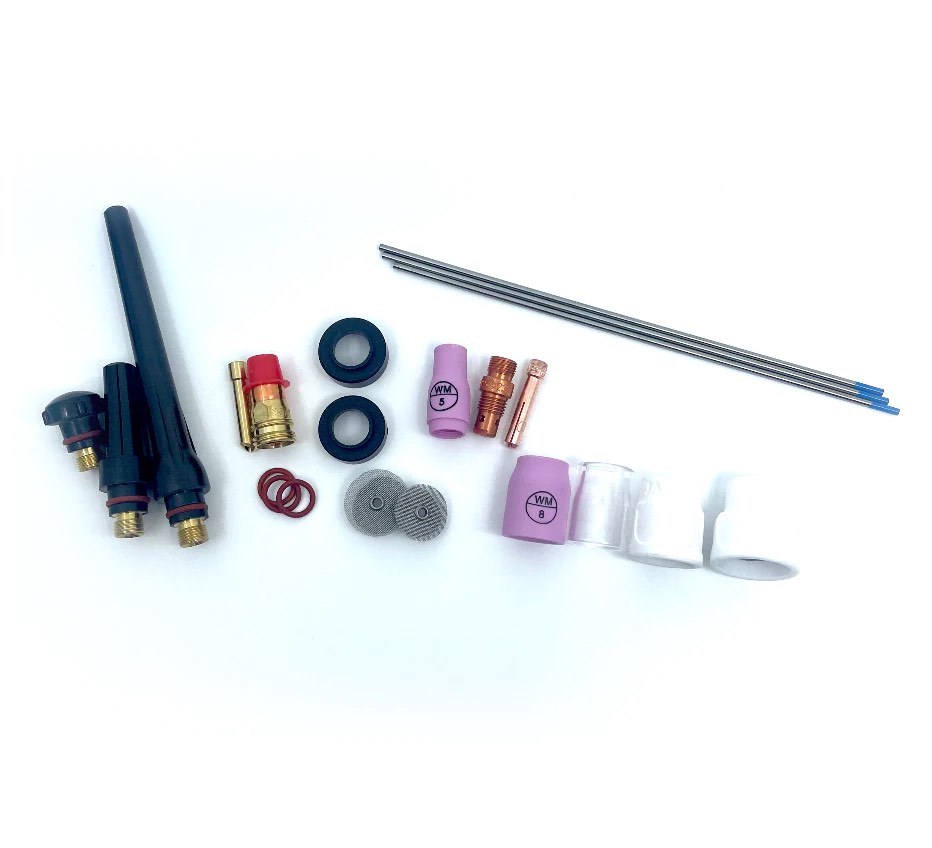
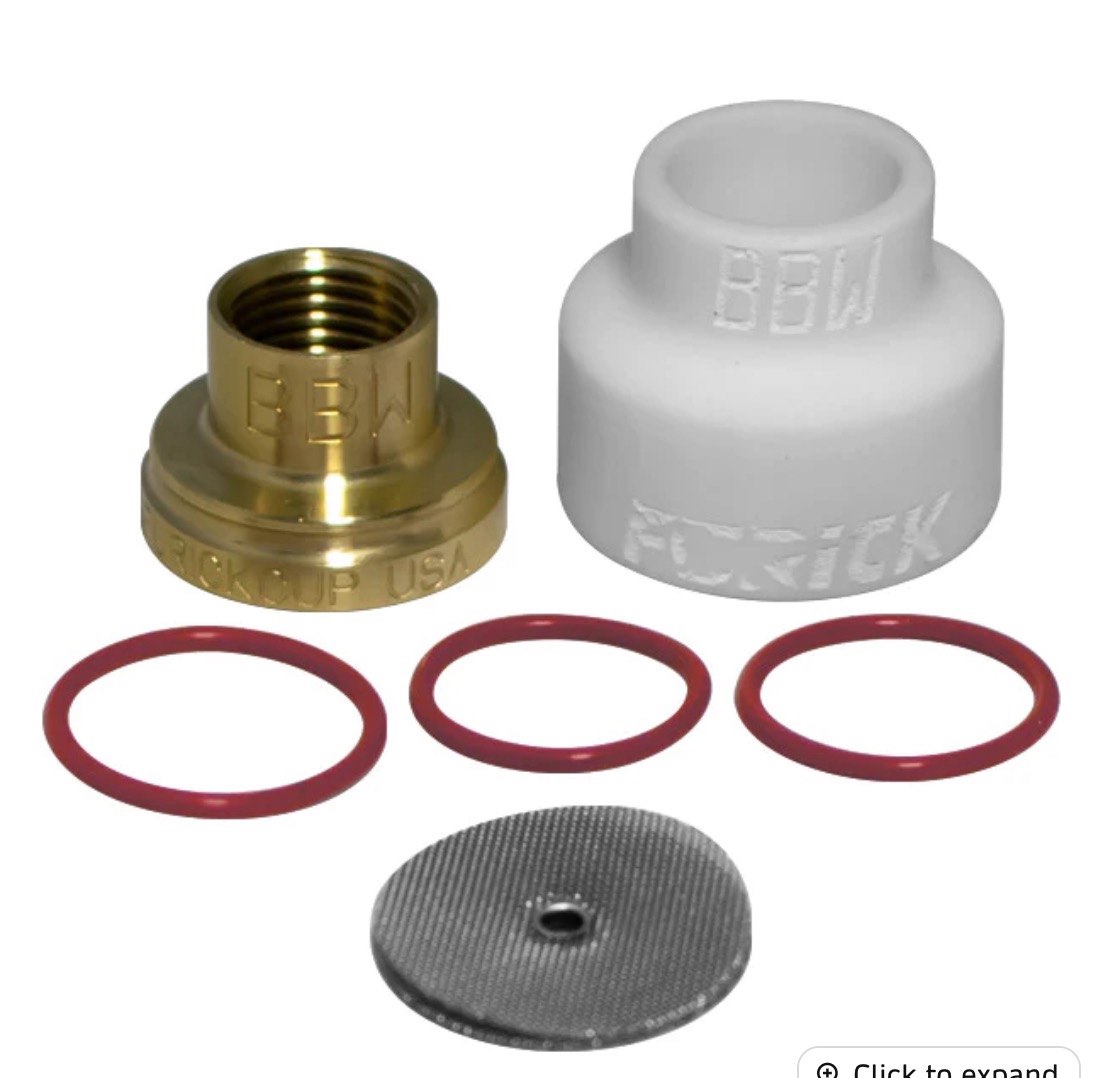
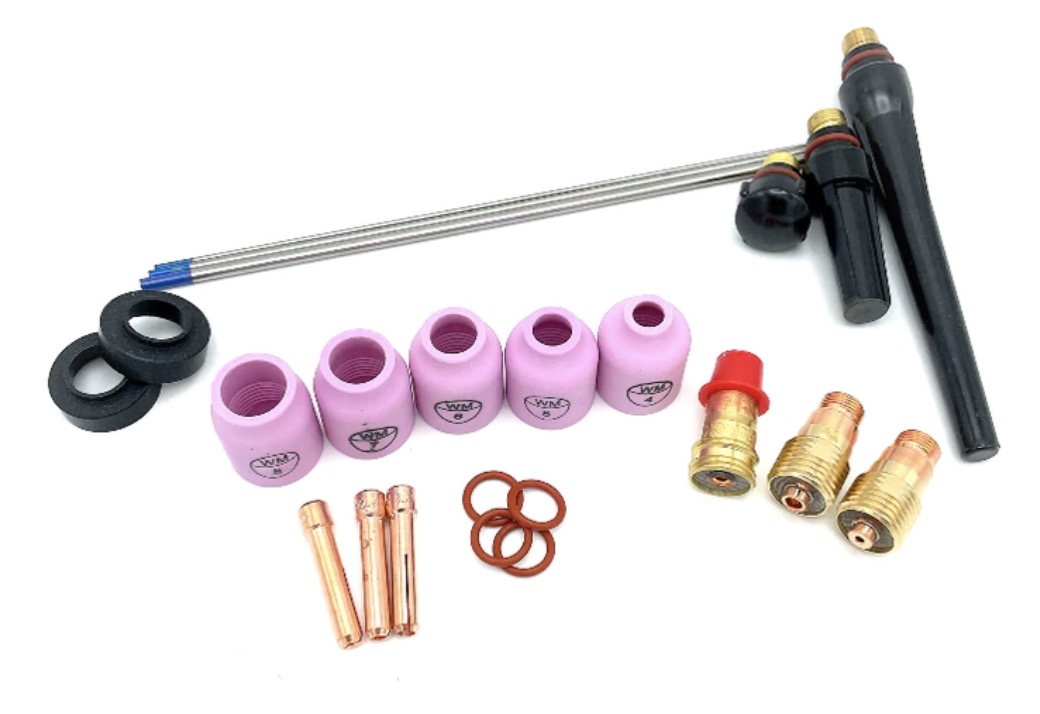
...Introducing the New WeldMonger Challenger TIG kit that includes the most frequently used Cups.
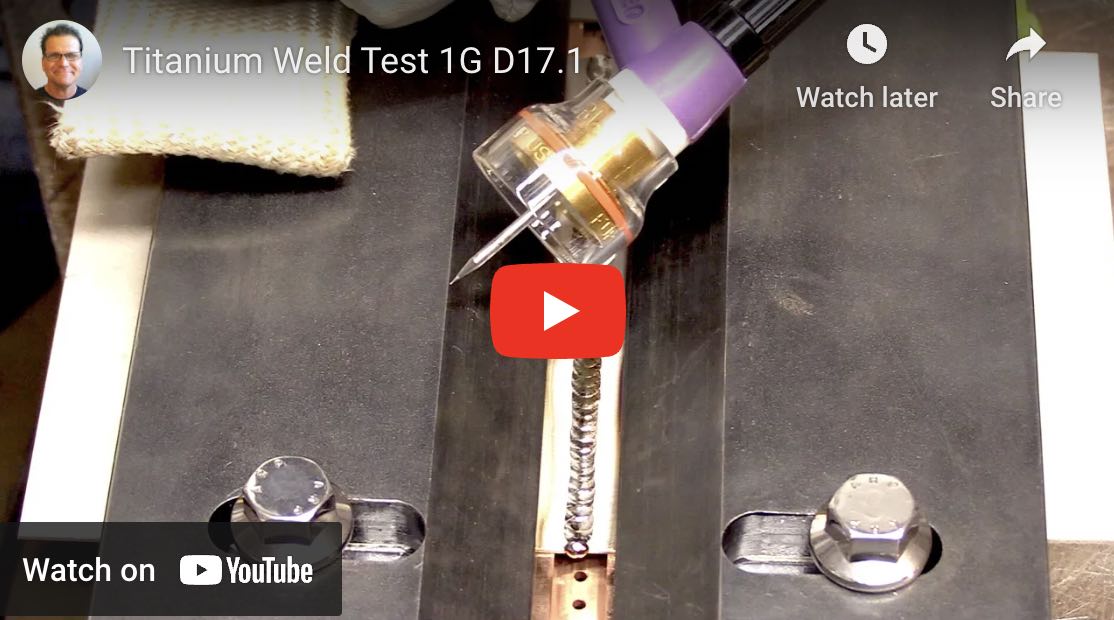
Group 6 Titanium Alloys 1G, 2g, 3g D17.1 weld tests
Why are 2g and 3g test welds used by aerospace MRO's to certify welders?
- Structural Integrity: In aerospace applications, welded components often bear significant structural loads and must withstand harsh environmental conditions. Different positions simulate real-world scenarios where welds may be required, ensuring that the welds maintain their structural integrity and do not compromise the safety of the aircraft.
- Versatility: Aircraft components come in various shapes and sizes, and welders must be able to adapt to different welding situations. By certifying welders in multiple positions like 2G (horizontal groove) and 3G (vertical groove), MRO companies ensure that welders can handle a wide range of welding orientations and challenges.
- Quality Assurance: Certifying welders in various positions helps maintain high-quality standards. Different positions require welders to demonstrate their skill and precision in welding, ensuring that welds meet specified quality requirements, such as penetration depth, fusion, and minimal defects.
- Regulatory Compliance: Aerospace welding is highly regulated by aviation authorities, such as the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) in the United States. These authorities often specify the positions in which welders must be certified to ensure compliance with safety and quality standards. AWS D17.1 is considered the main guide and specification and requires anyone who welds on aircraft or engine components to by qualified to D17.1 requirements.
- Consistency and Reliability: Aerospace MRO companies rely on welders to consistently produce high-quality welds. By certifying welders in different positions, companies can be confident that their welders can consistently perform well, regardless of the welding orientation.
- Skill Development: Welders need continuous training and development to stay up-to-date with the latest techniques and technologies. Certifying welders in various positions encourages skill development and helps them become more versatile and adaptable in their welding practices.
In summary, aerospace MRO companies use different welding positions like 2G and 3G to certify welders because of compliance and because it ensures the safety, quality, and reliability of welded components in aircraft. These positions simulate real-world scenarios while also encouraging welders to develop their skills and versatility to meet the stringent demands of the aerospace industry.