TIG stainless
This first video below provides most of what you need to know when it comes to tig stainless steel.
- heat input
- back purging
- travel speed
- keep stainless stainless
Tips for TIG stainless like back purging and pulse settings
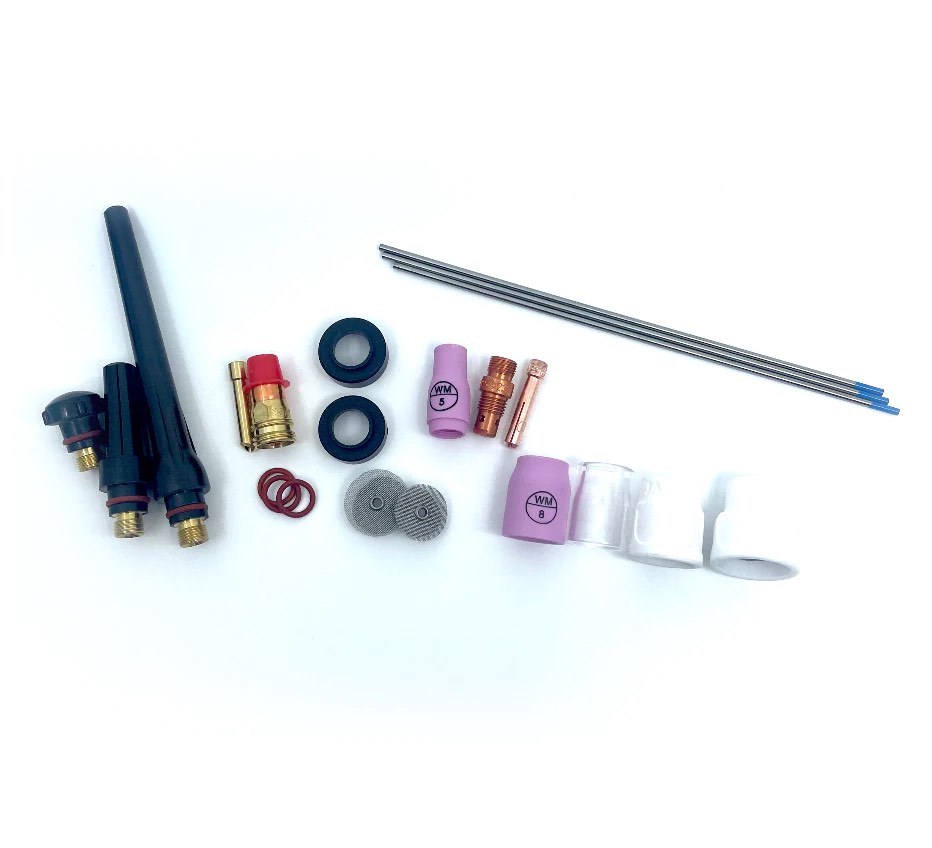
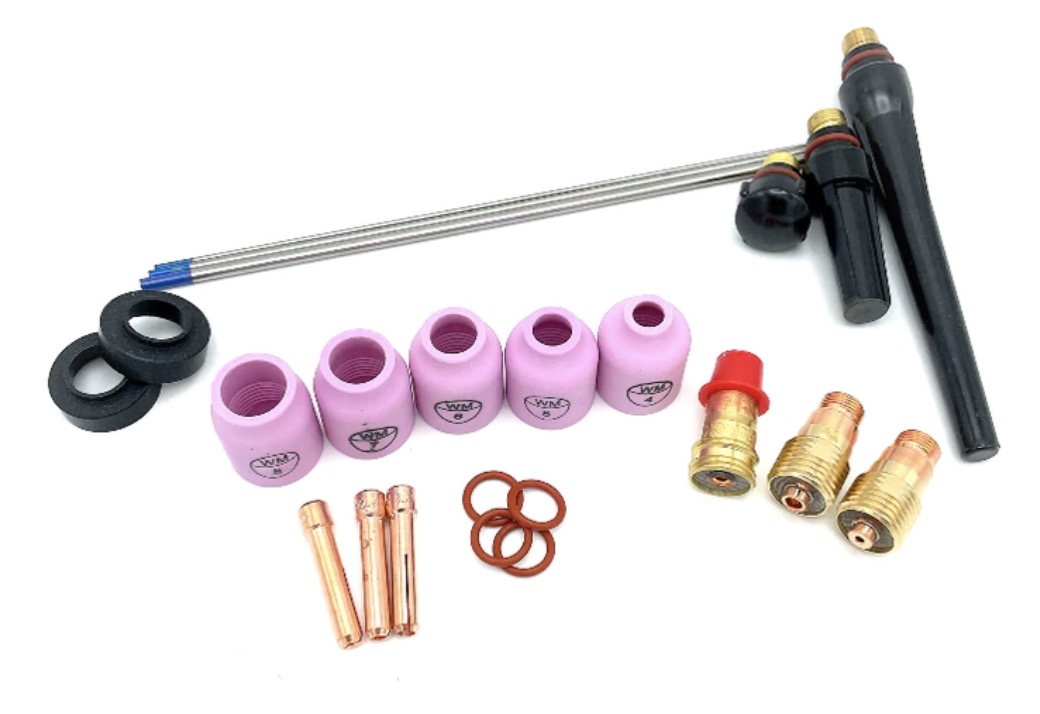
What is the best cup for tig stainless?
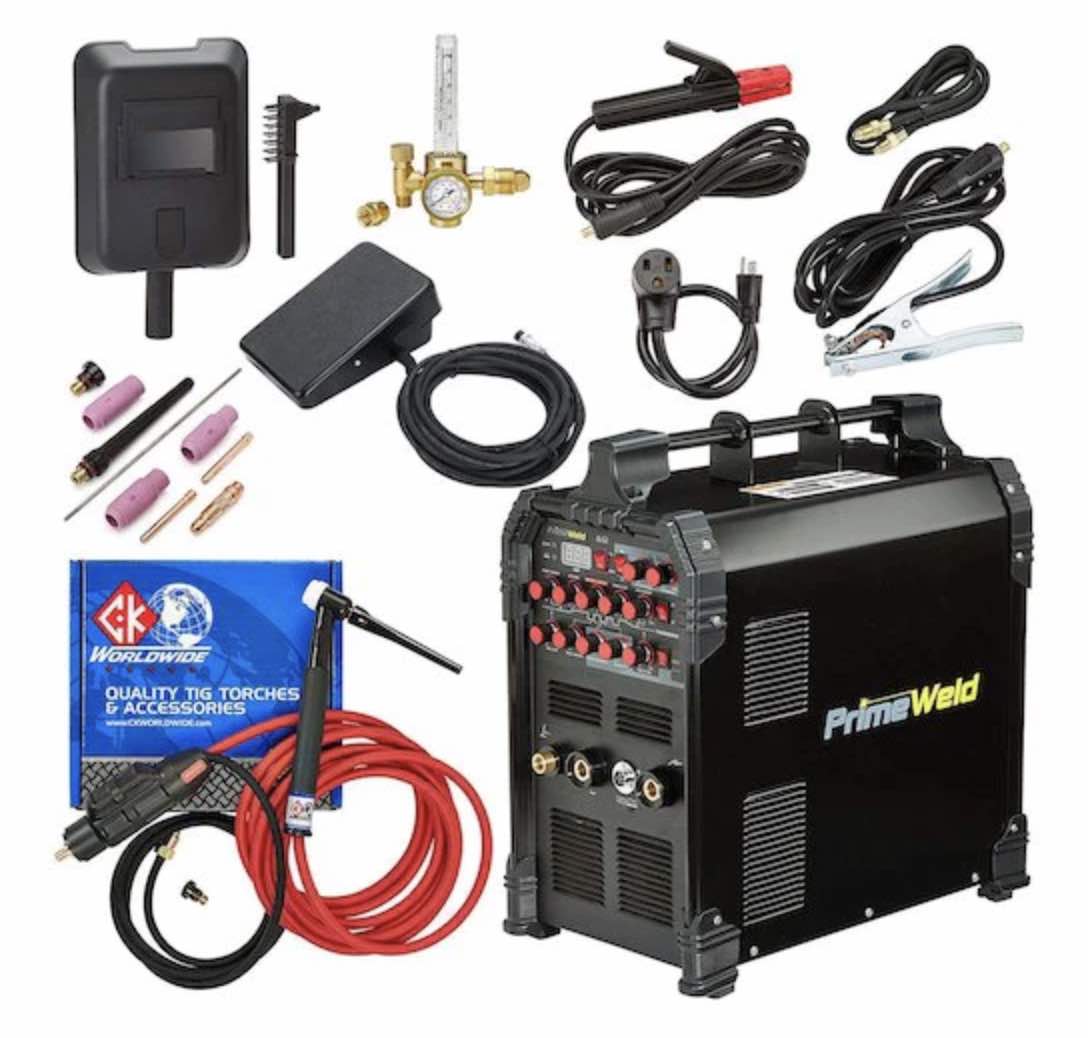
Learn more about this affordable tig welder with bonus kit at weldmonger.com
The best cups for tig welding stainless depends on a few factors like thickness, shape, etc.
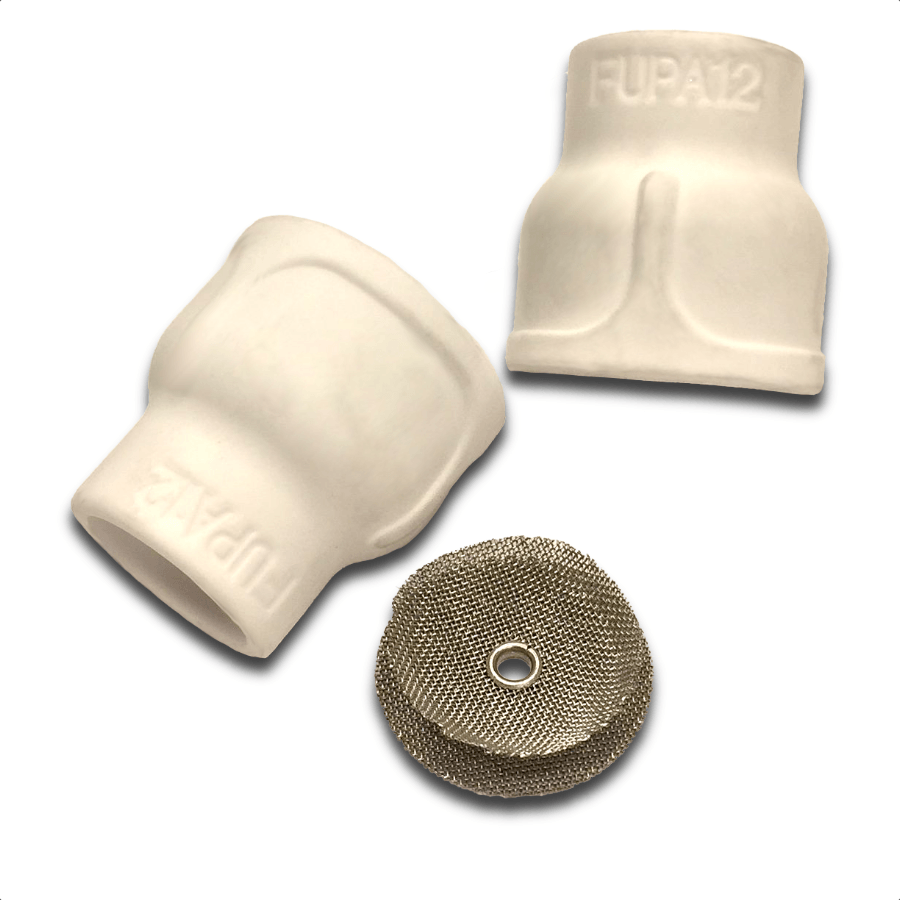
But I have come to really like the furick jazzy10 ceramic cup for tig stainless.
It really depends on what you are welding.
there are times when a #8 gas lens cup works fine for stainless but a jazzy 10 with secondary diffuser screens jumps you up to another level of gas shielding
What are things that make the biggest difference with TIg stainless?
TIG welding stainless steel requires careful attention to several key factors to achieve high-quality results. Here are the most critical aspects that make the biggest difference:
### 1. **Shielding Gas**
- **Pure Argon**: Use high-purity argon gas to shield the weld area from atmospheric contamination. This prevents oxidation and ensures a good weld.
- **Back Purging**: For full penetration welds, back purging with argon is needed to protect the penetration side of the weld from oxidation and contamination.
### 2. **Cleanliness**
- **Surface Preparation**: Stainless steel should be thoroughly cleaned before welding. Remove any dirt, oil, grease with a stainless steel brush or solvent like acetone. Contaminants can cause weld defects and reduce corrosion resistance.
- **Tungsten Electrode**: A 3/32" 2% lanthanated tungsten is probably the most versatile type and size tungsten for tig welding stainless up to around 200 amps.
Whatever tungsten you use, keep the tungsten electrode clean and sharp to maintain a stable arc and prevent contamination of the weld pool.
### 3. **Heat Control**
- **Low Amperage**: Use the lowest amperage setting that will achieve adequate penetration. Excessive heat can cause warping, burn-through, and reduce corrosion resistance.
- **Pulsed Welding**: Consider using pulsed current to control heat input more effectively. Pulsing allows better control over the weld pool and minimizes heat-affected zones.
- **Intermittent Welding**: Allow the material to cool between passes to prevent overheating and distortion.
### 4. **Welding Technique**
- ** Travel Speed**: travel speed has a lot to do with heat input.
If you travel too slow and get moving too slow, heat can build up and you just cant outrun it.
Establish the puddle quickly and get the puddle moving within 2-3 seconds.
Maintain a consistent travel speed to ensure uniform bead appearance and penetration. Inconsistent speed can lead to defects like undercutting and uneven welds.
- **Proper Torch Angle**: Hold the torch at a 15-20 degree angle to the workpiece. This helps to direct the arc and shielding gas correctly, ensuring proper weld bead formation.
- **Filler Rod Technique**: Use the correct diameter filler rod and add it steadily to the leading edge of the weld pool. This helps maintain a clean and strong weld.
### 6. **Post-Weld **
- **Cleaning**: Remove any residual oxides or discoloration from the weld area using a stainless steel brush or appropriate chemical cleaner. This helps maintain the corrosion resistance of the stainless steel.
- **Passivation**: Sometimes, codes or procedures might requiring a passivating treatment to the weld area to restore the protective chromium oxide layer. This enhances the corrosion resistance of the welded joint.
### Summary
Achieving high-quality TIG welds on stainless steel involves meticulous preparation, careful control of heat input, and consistent welding techniques. By focusing on these critical factors, welders can produce strong, clean, and corrosion-resistant welds.