Stainless TIG welding
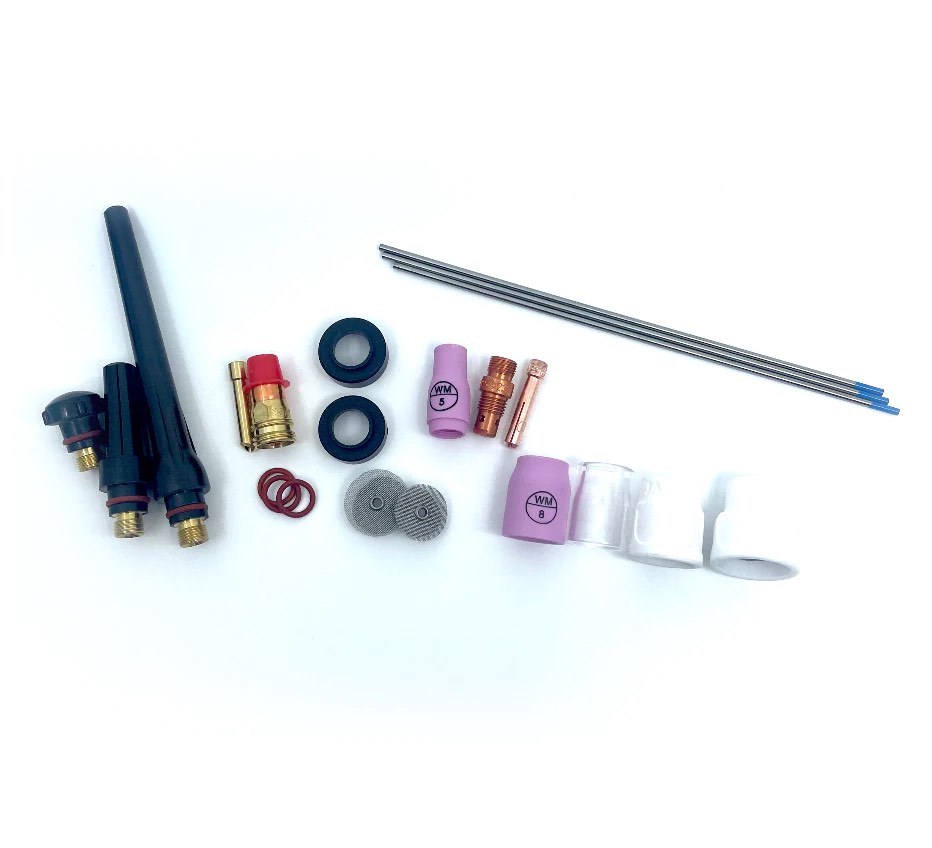
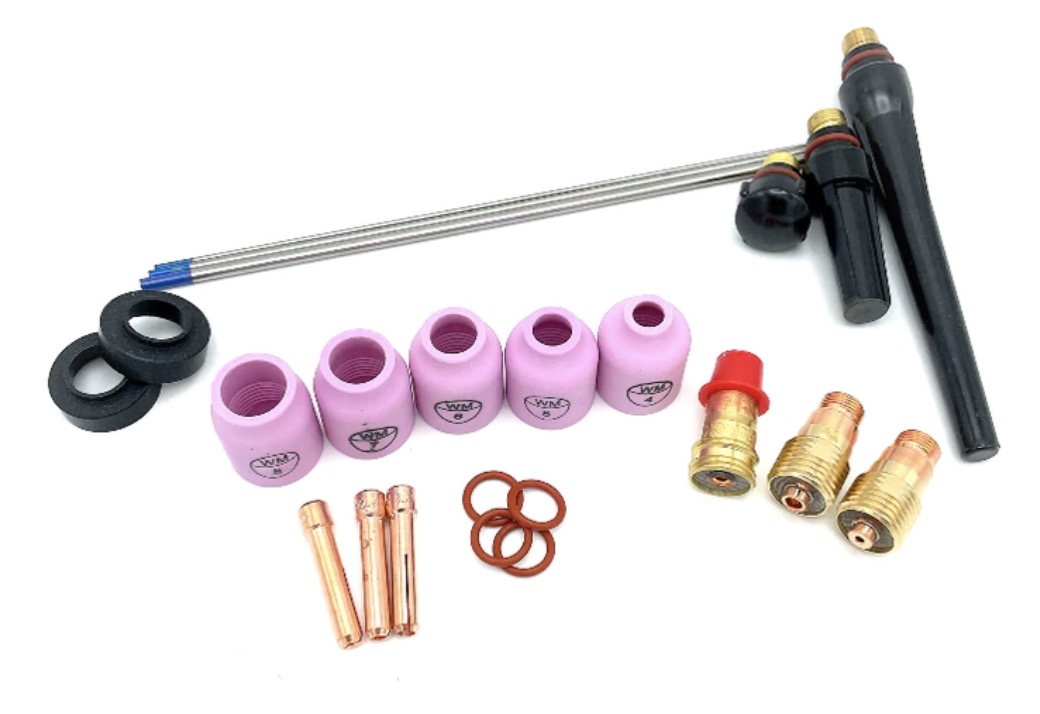
...Introducing the New WeldMonger Challenger TIG kit that includes the most frequently used Cups.
When it comes to stainless tig welding, there are several key things that will help maintain the stainless properties of the stainless steel you are welding as well as make for a good looking weld.
- Use the right cup
- use the right tungsten
- use the right filler rod
- get good gas shielding on the front and back if needed
- don't crap up the weld with carbon particles
Use the right cup
stainless loves argon shielding.
So what is the right cup to provide that argon shielding?
A gas lens cup really helps for stainless tig welding and a specialty gas lens cup like a furick jazzy 10 or furick 12 can make a huge difference in discoloration.
What is the best tungsten for stainless tig welding?
There are so many choices available.
E3, 2% thoriated, 2% ceriated, 2% lanthanated, etc.
but if you want to simplify things , 2% lanthanated tungsten is a great all purpose tungsten for stainless as well as all other metals.
If you find yourself tig welding stainless most of the time, then 2% ceriated or LayZr tungsten will be a great choice.
Use the right filler rod
TIG welding filler metal is in stock at Weldmonger.com
TIG welding filler metal is in stock at Weldmonger.com
Usually, a matching filler rod is the best choice for tig welding stainless steels.
a good example of this would be tig welding 316L stainless where 316L filler rod would be the choice.
But there are a few exceptions.
For example 304 stainless is typically welded using ER308L filler rod.
Another example is 303 stainless...which is a free machining grade of stainless that contains sulfur to assist in machining. 303 stainless is not recommended across the board for welding but it can be welded for certain applications and ER308L is a good choice.
here is a link to help you choose the best tig rod for stainless steel
Gas shielding on the front and the back
Gas shielding on the front or welded side is accomplished using the right cup.
But for the back side..the penetration side, either backing or argon shielding is needed for best results.
Argon purge boxes can be made to allow for a purge on the back or penetration side but a copper or aluminum backing can also be effective.
Don't crap up the weld with carbon particles
Grinding wheels, flap discs, files, and stainless wire brushes should all be dedicated to stainless steel.
Using them on carbon steel and then on stainless can impregnate carbon particles into the stainless.
when that happens, stainess can actually rust.
Keep stainless stainless by dedicating grinding wheels, files, and brushes to be used only on stainless steels.hja
Avoiding loss of stainless properties aka corrosion resistance
When TIG welding stainless steel, preserving its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties should be one of the main priorities
Here are three main ways to avoid the loss of these properties:
1. Control Heat Input
Heat input is a critical factor in maintaining the stainless properties of the material. Excessive heat can lead to sensitization, where chromium carbides form at grain boundaries, reducing corrosion resistance.
Heat input is affected greatly by travel speed as well as time spent establishing a puddle.
When tig welding stainless, get your puddle established and get the puddle moving within 3 seconds.
Lingering around too long allows too much heat to build up in one place and contributes to excess heat input which can lead to sensitization and distortion.
To control heat input:
Use Proper Amperage: proper amperage does not necessarily mean low amperage. Ensure the welding current is appropriate for the thickness of the stainless steel but high enough to establish a puddle quickly. With a foot pedal, you can benefit from more amperage to establish the puddle and a bit less amperage after that.
Maintain a Steady Travel Speed: Keep a consistent welding speed to avoid overheating any particular area.
Pulsed TIG Welding: Pulsing the current can help manage heat more effectively by providing intervals of high and low current.
2. Use the Correct Filler Material
Selecting the right filler material is essential to maintain the stainless properties of the weld:
Use the recommended Filler for the Base Metal: Use a filler rod that closely matches the composition of the stainless steel being welded. For example, if welding 304 stainless steel, use a 308L filler rod.
Low Carbon Content: Use low-carbon fillers (indicated by an "L" in the grade, like 308L) to minimize the risk of carbide precipitation and sensitization.
3. Shielding Gas and Coverage Proper gas coverage are big factors to prevent oxidation and contamination:
Use High-Purity Argon: Ensure that high-purity argon gas (99.99% pure) is used as the shielding gas to prevent contamination from the atmosphere.
Maintain Adequate Gas Flow: Proper gas flow rates should be maintained to provide effective shielding. Flow rates for the torch gas are largely determined by the size of the cup and type of cup used.
As a general rule of thumb, multiply cup size by 2-3 cfh to be in the ball park. Of course this depends on the level of drafts or breeze in the work area but it is a starting place.
Gas Lenses and Backup Shielding: Use a gas lens to improve gas coverage on the frond side and for full penetration welds, use a purge shielding on the back side.
A dual flowmeter makes purging very convenient
By controlling heat input, using the correct filler material, and ensuring proper shielding gas coverage, you can effectively maintain the corrosion resistance and mechanical properties of stainless steel during TIG welding.